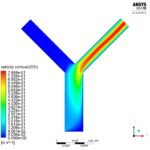
Analysis of the Effect of Atherosclerosis with the Changes of Hematocrit: A Computational Study on the Hemodynamics of Carotid Artery
Nihal Ahmed, Ashfaq Ahmed, Sakan Binte Imran
Atherosclerosis is a state wherein plaque (fat, cholesterol, and different substances) develops inside the veins that in the end prompts carotid artery stenosis, which is a phase of narrowing in the huge courses situated on either side of the neck that convey blood to the brain, face, and head. Carotid stenosis is regularly connected with perpetual injury of an aspect of the brain (strokes) because of the loss of its blood flexibility. For instance, ischemia generally brings about serious handicaps or demise. Hematocrit or pressed cell volume (PCV) is the volume of red blood corpuscles according to that of the entire blood. The reason for our exploration is to carry out a Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) investigation of the bloodstream with the rate changes of hematocrit to examine the hemodynamic and physiological conduct of atherosclerosis. Our examination a developed 2D calculation model that has been investigated utilizing Finite volume technique (FVM) for interesting phases of atherosclerosis. The point of this investigation is to investigate the social bits of knowledge into the velocity slope, wall shear stress, and pressure gradient of the carotid corridor under various rates of hematocrit and various phases of atherosclerosis. The investigation introduced convincing distinctions in these boundaries, which can be utilized to recognize the atherosclerosis development.
Numerical modeling of Marangoni convection in the presence of external magnetic field
Raisa Akhtaruzzaman, Ashfaq Ahmed, Md. Quamrul Islam, Suman Saha, Mohammad Nasim Hasan
The present numerical study has been conducted to explore on the effects of external magnetic field at different angle of inclination on the flow driven by the combined mechanism of buoyancy and thermo-capillary flow in an open enclosure. The enclosure is provided with localized heating from below and symmetric cooling is assumed from sides. Along the free surface on the top of the enclosure, the surface tension varies with temperature difference which is known as the Marangoni effect and also called the thermo-capillary effect. The governing equation of the system (i.e. mass, momentum and energy) are presented in the non-dimensional form along with necessary boundary conditions and hence been solved numerically by Galerkin finite element method (FEM) with triangular discretization system. The effect of pertinent parameters such as Hartmann number (0 < Ha < 100), angle of inclination of the magnetic field (0° < ϕ < 90°), Grashof number (10³ < Gr < 10⁶), Marangoni number (-100 < Ma < 100) and Prandtl number (0.7 < Pr < 7) on the isotherms, streamlines inside the enclosure as well the heat transfer performance of the system have been explored for various parametric conditions of the system. One key observation is flow field changes drastically with angle of inclination in the presence of the Marangoni effect. And also the heat transfer increases at higher Prandtl number and Grashof number.
